Analisis Model Supply pada Jaringan Sistem Kelistrikan di Fakultas Teknik Universitas Udayana Bukit Jimbaran
Abstract
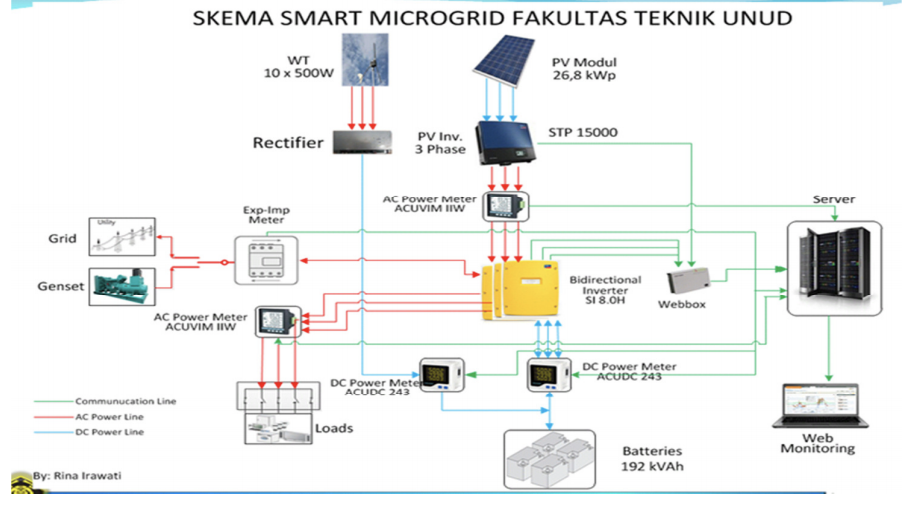
The addition of the power source to the main network is one way to improve the quality of electric power system, network reliability and to reduce power losses. The addition of the energy source is a smart microgrid system. The smart microgrid technology is a technology that uses renewable energy as a main supply. Smart microgrid system consists of a 24 kWp solar power, Wind Turbine 5 kWp system 240 kVAh battery and genset 20 kVA. The smart microgrid system to be implemented at the Engineering Faculty of Udayana University. The results showed the power loss (losses) on the electrical grid at FT Bukit Jimbaran before the advent of smart microgrid system to the network, acquired losses of 6.4 kW or 3.68% of the total load when the network is supplied from PLN and after the inclusion of smart microgrid system and generator sets to the grid obtained by losses of 1.2 kW or decreased losses of 0.69% of the total expenses of 173.54163 kW. Reliability indices obtained at the Technical University of Udayana network after the entry smart microgrid system when interconnected with PLN namely SAIFI: 0.1029, SAIDI: 1.9229 hours / customer, and CAIDI: 18.686 hours / interruption.
Downloads
References
[1] I. N. S. Kumara, W. G. Ariastina, I. W. Sukerayasa and I. A. D. Giriantari, Perkembangan Energi Terbarukan di Bali. 2014. On the potential and progress of renewable electricity generation in Bali," 2014 6th International Conference on Information Technology and Electrical Engineering(ICITEE),pp.1-6 doi:10.1109/ICITEED.2014.7007994.
[2] PT. LEN Industri (Persero),PLTS On Grid 20 kWp Gil Trawangan Go Green, Buletin LEN, No.8 (November 2011)
[3] I N. S. Kumara, W.G. Ariastina, I W. Sukerayasa and I. A. D. Giriantari. “1 MWp Grid Connected PV Systems in the Village of Kayubihi Bali; review on location’s characteristics and its technical specifications”.International Conference on Information Technology and Electrical Engineering (ICITEE) 2013. 10.1109/ICITEED. 2013.6676258.
[4] I. M. A. Nugraha., I.A.D. Giriantari., I.N.S. Kumara. 2013. Studi Dampak Ekonomi dan Sosial PLTS Sebagai Listrik Pedesaan Terhadap Masyarakat Desa Ban Kubu Karangasem. Prosiding Conference on Smart Green in Electrical and Information Systems, Bali, A-010, (14-15 November 2013).
[5] I.G.A. Andita Putra., I.A.D. Giriantari., I.N.S. Kumara. 2015. Studi Sistem Pengelolaan PLTS 15kW Stand Alone dengan Metode Kano di Dusun Yeh Mampeh Kabupaten Bangli. Teknologi Elektro, Vol.14, No. 1 (Januari-Juni)
[6] I.N.S. Kumara. M. Ashari, A. S. Sampeallo, A. A. G. A Pawitra. (In Press). “Simulated Energy Production and Performance Ratio of 5 MW Grid-connected Photovoltaic under Tropical Savannah Climate in Kupang Timor Island of Indonesia”. International Journal of Engineering and Technology Innovation.
[7] Darma Putra, Krisna. 2015, Perencanaan Sistem Jaringan Mikro (Microgrid) dengan Supply dari Pembangkit Listrik Tenaga Surya (PLTS) dan Generator Set di Jurusan Teknik Elektro Universitas Udayana. Teknologi Elektro, Vol.14. No. 2 (Juli – Desember): 69-74
[8] Nyserda.Available:https://www.nyserda.ny.gov/All-Programs/Programs/NY-Prize/Resources-for-applicants/Microgrids-101. [online]
[9] The U.S. Department of Energy’s Microgrid Initiative,DOE Microgrid Workshop Report,August.30-31,2011,[online].Available:https://energy.gov/sites/prod/files/Microgrid%20Workshop%20Report%20August%202011.pdf
[10] IAD Giriantari, Rina Irawati. Smart Microgrid System with Supply from Hybrid. ICGTEIS2016. Bali, Indonesia:Udayana University, 2016.
[11] Bilinton, A dan Ronald. Reliability Evaluation of Power System.2nd
Ed. New York:PlenumPress, 1996.
[12] Rina Irawati, Pengembangan Smart Microgrid Untuk Integrasi Pembangkit berbasis Energi Terbarukan,Jakarta: Kementrian Energi dan Sumber Daya Mineral, Focus Group Disscussion CORE Universitas Udayana,Oktober, 2016.
[13] Hartati, Rukmi S, Sukerayasa I Wyn.,Setiawan I Nym., Ariastina Wyn Gd. 2007. Penentuan Angka Keluaran Untuk Evaluasi keandalan Sistem Distribusi Tenaga listrik. Teknologi Elektro, Vol.6, No.2 (Juli-Desember).
[14] SPLN (Standar Perusahaan Listrik Negara) 59:1985. Keandalan Pada Sistem Distribusi 20 kV dan 6 kV. 1985.
[15] Iswadiah, Sudibyo, Setiawan, E.A., 2010. Analisis Kinerja Pembangkit Listrik Energi terbarukan Pada Model Jaringan Listrik Mikro Arus Searah. Politeknologi, Vol 9. No.2.
Keywords

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License