Potensi Pemanfaatan Atap Tribun Stadion Kapten I Wayan Dipta Gianyar sebagai PLTS Rooftop
Abstract
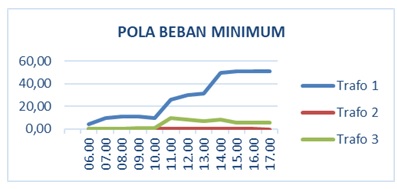
Captain I Wayan Dipta stadium rooftop power plant is designed as an additional power supply to meet the stadium's electrical load needs. Roof plts design using 2 scenarios. Scenario 1 has a capacity of 83,300 Wp with a solar module of 238 units and a 2-unit inverter generating 112,321 kWh/year of energy and will supply the day load of transformers 2 and 3 stadiums of 35,470 kWh/year. Scenario 2 with a capacity of 156,800 Wp with a solar module of 448 units and 4 inverters generates 211,458 kWh/year of energy and will supply the day load of transformer 1 stadium at 100,919 kWh/year. Scenario 1 investment cost of Rp.1,178,760,000 with total income up to 25 years amounting to Rp.1,090,635,084 while in scenario 2 costs investment amounting to Rp.2,237,860,000 and income up to the 25th year amounting to Rp.3,126,761,273 in economic feasibility analysis using NPV, PI, and the DPP is only scenario 2 which can be said to be feasible because in the 25th year the income is greater than the investment, while in scenario 1 the income will be worth the same as the investment in the 29th year. This means the system in scenario 1 is not feasible because it has a DPP longer than the lifespan of the project.
Downloads
References
[2] Direktoral Jenderal Ketenagalistrikan Kementerian Energi dan Sumber Daya Mineral. 2013.
[3] I. N. S. Kumara, W. G. Ariastina, I. W. Sukerayasa and I. A. D. Giriantari, "On the potential and progress of renewable electricity generation in Bali," 2014 6th International Conference on Information Technology and Electrical Engineering (ICITEE), Yogyakarta, 2014, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/ICITEED.2014.7007944.Peraturan Gubernur Bali Nomor 45 Tahun 2019. Tentang Bali Energi Bersih. 2019.
[4] I.N.S Kumara, I.A.D. Giriantari, W.G. Ariastina, W. Sukerayasa, N. Setiawan, C.G.I. Partha, “Peta Jalan Pengembangan PLTS Atap : Menuju Bali Mandiri Energi, Center for Community Based Renewable Energy (CORE) Universitas Udayana, Greenpeace Indonesia, Bali, 2019.
[5] Peraturan Presiden no, 22 tahun 2017. “Rencana Umum Energi Nasional,” 2017.
[6] N.S. Gunawan, I.N.S Kumara, R. Irawati, “Unjuk Kerja Pembangkit Listrik Tenaga Surya (PLTS) 26,4 kWP pada Sistem Smart Microgrid UNUD. Jurnal Spektrum, [S.I.], v. 6, n. 3, p. 1-9, sep. 2019.
[7] M.R. Wicaksana, I.N.S Kumara, I.A.D Giriantari, “Unjuk Kerja Pembangkit Listrik Tenaga Surya Rooftop 158 kWp pada Kantor Gubernur Bali,” Jurnal Spektrum, [S.I], v. 6, n. 3 p.-107-113, Sep. 2019
[8] H. Kristiawan, I.N.S Kumara, I.A.D Giriantari, “Potensi Pembangkit Listrik Tenaga Surya Atap Gedung Sekolah di Kota Denpasar,” Jurnal Spektrum, [S.I], v. 6, n. 4, p. 66-70, dec. 2019.
[9] K. Sumariana, I.N.S Kumara, W.G. Ariastina, “Desain dan Analisa Ekonomi PLTS Atap untuk Villa di Bali,” Majalah Ilmiah Teknologi Elektro, 18(3), 337-346. doi:10.24843/MITE.2019.v18i03.P06. 2019
[10] D. Tan, A.K. Seng, “Handbook for Solar Photovoltaic Systems,” Singapore : Energy Market Authority. 2014.
[11] I.G.A.A Putra, I.A.D Giriantari, I.N.S Kumara, “Studi Sistem Pengelolaan PLTS 15 kW Stand Alone dengan Metode Kano di Dusun Yeh Mampeh Kabupaten Bangli” Jurnal Teknologi Elektro Unud. Vol. 14 No. 1. 2015
[12] ABB, “Technical Application” Paper No. 10 Photovoltaic Plants. s.l.:s.n. 2010.
[13] S. Soulayman, W. Sabbagh, “Solar collector optimum tilt and orientation,” Open Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy 2, 1–9. 2015
[14] J.W. Agung, M. Irwan, I. Muallim, S. Supartio,“Perencanaan PLTS Untuk Wilayah Kabupaten Gowa Dusun Pakkulompo Provinsi Sul-Sel,” Makalah. Politeknik Negeri Ujung Pandang. Makassar. 2012.
[15] H.J. Patricia, “Analisis Keekonomian Kompleks Perumahan Berbasis Energi Sel Surya (Studi Kasus: Perumahan Cyber Orchid Town Houses, Depok),” FT UI. 2012.
[16] Kashmir & Jakfar, “Studi Kelayakan Bisnis” Edisi Revisi, Penerbit PT. Desindo Putra Mandiri, Jakarta. 2017.
[17] PT. PLN (Persero) Area Bali Timur. “Data Beban Stadion Kapten I Wayan Dipta Gianyar Bali” 2020.
[18] L.E. Bien, dkk, “Perancangan system Hibrid Pembangkit Listrik Tenaga Surya Dengan Jala-Jala Listrik PLN Untuk Rumah Perkotaan,” Jakarta: Teknik Elektro Universitas Trisakti. 2008
[19] P.A. Sujana, I.N.S Kumara., I.A.D Giriantari., “Pengaruh Kebersihan Modul Surya Terhadap Unjuk Kerja PLTS,” E-Journal Spektrum Vol. 2, No. 3. 2015.
[20] R. Hariyati, M.N. Qosim, A.W. Hasanah, “Konsep Fotovoltaik Terintegrasi On Grid dengan Gedung STT.PLN” Energi dan Kelistrikan : Jurnal Ilmiah Vol. 11, No. 1. 2019.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License