Audit Sistem Informasi E-Kinerja Dinas Kependudukan Dan Pencatatan Sipil Kota Denpasar
Abstract
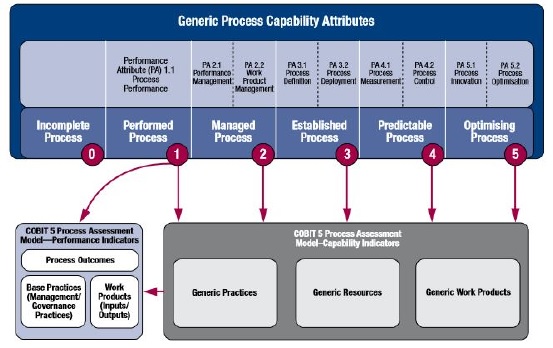
Abstract— Civil Servants or abbreviated as PNS represent countries that have a role in carrying out their duties to achieve the goals of the State. Contributions made by civil servants through performance affect the progress and achievement of a government agency. Staffing management at government agencies has been processed by utilizing information technology. E-Kinerja is a breakthrough by the government to measure the productivity of civil servants against responsibilities towards the main tasks and functions in achieving the objectives of government. The E-Performance information system each civil servant processes the employee performance target data input process, which is an agenda to be carried out by PNS, based on the PNS Work Behavior. The E-Performance information system of each civil servant process the employee performance targets the input data process, which is an agenda to be carried out by civil servants, based on the PNS Work Behavior. The capability of the E-Kinerja information system for staffing management needs to be evaluated. E-Performance information system audits can provide an overview, evaluation and identification of the use of information technology can provide results in terms of staffing management. COBIT 5 Framework is a collection of procedures that can meet the needs of governance and management to achieve the goals of an organization. In this research the E-Kinerja information system reaches an average value of 3.67 at level 4 (Predictble Process). Indicates that the planning of the E-Kinerja information system at the Denpasar City Population and Civil Registry Office has achieved the expected goals.
Downloads
References
[2] P. Indonesia, Ed., KEBIJAKAN DAN STRATEGI NASIONAL PENGEMBANGAN E-GOVERNMENT. Indonesia: Intruksi Presiden Republik Indonesia Nomor 3 Tahun 2003, 2003.
[3] PERATURAN PEMERINTAH REPUBLIK INDONESIA NOMOR 30 TAHUN 2OL9 TENTANG PENILAIAN KINERJA PEGAWAI NEGERI SIPIL. Indonesia: Pemerintah Indonesia, 2019.
[4] Dinas Kependudukan dan Pencatatan Sipil Kota Denpasar, PROFIL DINAS KEPENDUDUKAN DAN PENCATATAN SIPIL KOTA DENPASAR. Indonesia: Dinas Kependudukan dan Pencatatan Sipil Kota Denpasar, 2019.
[5] Pemerintah Republik Indonesia, PERATURAN PRESIDEN REPUBLIK INDONESIA NOMOR 95 TAHUN 2018 TENTANG SISTEM PEMERINTAHAN BERBASIS ELEKTRONIK. Indonesia: Pemerintah Republik Indonesia, 2018.
[6] UNDANG-UNDANG REPUBLIK INDONESIA NOMOR 43 TAHUN 1999 TENTANG PERUBAHAN ATAS UNDANG-UNDANG NOMOR 8 TAHUN 1974 TENTANG POKOK-POKOK KEPEGAWAIAN. Indonesia: Pemerintah Indonesia, 1999.
[7] UNDANG-UNDANG REPUBLIK INDONESIA NOMOR 5 TAHUN 2014 TENTANG APARATUR SIPIL NEGARA. Indonesia: Pemerintah Indonesia, 2014.
[8] ISACA, A Business Framework for the Governance and Management of Enterprise IT. 2012.
[9] A. Agung, G. Aditya, and N. P. Sastra, “Framework Pengelolaan Infrastruktur TIK di Pemerintah Kabupaten Badung,” Maj. Ilm. Teknol. Elektro, vol. 17, no. 1, 2018.
[10] Safriwal, “REKOMENDASI PERBAIKAN MANAJEMEN TEKNOLOGI INFORMASI PADA DINAS SOSNAKERTRANS KABUPATEN SOLOK MENGGUNAKAN COBIT 5,” J. Masy. Telemat. dan Inf., vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 19–30, 2017.
[11] D. Nmae, “Evaluasi Infrastruktur Jaringan LAN OPD Pemerintah Provinsi Bali dengan COBIT 5 . 0,” vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 0–7, 2019.
[12] K. Budiarta, A. Iskandar, and M. Sudarma, “Audit Information System Development using COBIT 5 Framework (case Study: STMIK STIKOM Bali) Komang,” Int. J. Eng. Emerg. Technol., vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 1–5, 2016.
[13] B. Gamaliel et al., “KELOLA TEKNOLOGI INFORMASI MENGGUNAKAN COBIT 5 PADA PEMERINTAH SULAWESI UTARA,” E-Journal Tek. Inform., vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 1–8, 2017.
[14] A. Sumichan, I. M. G. Yudiyana, and I. M. Sudarma, “Audit with COBIT 5 Framework Focused on DSS Domains,” Int. J. Eng. Emerg. Technol., vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 67–71, 2018.
[15] S. Ranggi Praharaningtyas Aji, “PENILAIAN TATA KELOLA TEKNOLOGI INFORMASI PADA DINAS KESEHATAN KABUPATEN BANYUMAS MENGACU PADA KERANGKA KERJA COBIT 5,” J. Pro Bisnis, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 1–12, 2019.
[16] M. Hendayun, “Tata Kelola Teknologi Informasi pada Perguruan Tinggi Menggunakan Control Objective for Information & Related Technology ( COBIT ) 5,” J. Tek. Inform. dan Sist. Inf., vol. 3, no. April, pp. 206–216, 2017.
[17] D. Krisnandari, D. M. Wiharta, and N. P. Sastra, “Penerapan Teknologi Informasi dalam Reformasi Birokrasi pada Bidang Pendidikan,” Maj. Ilm. Teknol. Elektro, vol. 18, no. 2, 2019.
[18] S. D. Rehatta and A. D. Manuputty, “Measurement of the Maturity Level of IT Governance in Implementing Personnel Management Information System Using the MEA Domain COBIT 5 Framework In Regional Personnel, Education and Training Agency,” J. Inf. Syst. Informatics, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 123–135, 2019.
[19] S. Nella, S. Berlianna, and A. R. Perdanakusuma, “Evaluasi Tingkat Kapabilitas Sumber Daya Teknologi Informasi Pada Institut Teknologi Nasional Malang Menggunakan Kerangka Kerja Cobit 5,” J. Pengemb. Teknol. Inf. dan Ilmu Komput. Univ. Brawijaya, vol. 2, no. 10, 2018.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License