Analisa Sentiment Untuk Opini Alumni Perguruan Tinggi
Abstract
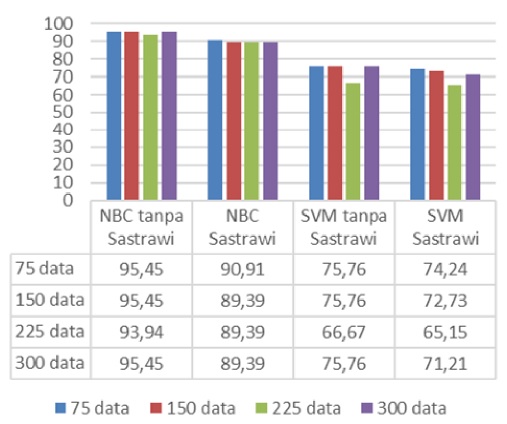
Opinion is one of the most important parts in decision making, in processing opinions require a thorough analysis process. Especially text-based opinion, where opinion in the form of opinions do not have a definite value limit for the input. Sentiment Analysis as a branch of knowledge from Text mining can be applied in the opinion analysis process in the form of text. Where opinions will be classified into 3 types of opinions, namely positive opinions, neutral opinions and negative opinions. This study grouped opinions from university graduated students using the SVM and NBC algorithms which in this study were divided into 3 main components, namely the input component, opinion grouping system, and output components.Opinion to be processed is data in the form of a * .csv format opinion file, which then conducts a grouping of opinions. Then the system produces output in the form of 3 types of opinions, namely, positive opinions, neutral opinions and negative opinions. In general, the accuracy results show the differences in the accuracy of each sentiment. From the test results generally shows the accuracy with the highest accuracy value in the NBC algorithm reaching 94.45 while the highest accuracy rate in the SVM algorithm reaches 75.76%.
Downloads
References
[2] G. A. Buntoro, “Sentiments Analysis for Governor of East Java 2018 in Twitter,” SinkrOn, vol. 3, no. 2, p. 49, Dec. 2019.
[3] E. I. Setiawan, “Komparasi algoritma untuk analisa sentimen review produk pada twitter,” vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 7–14, 2015.
[4] N. D. Putranti and E. Winarko, “Analisis Sentimen Twitter untuk Teks Berbahasa Indonesia dengan Maximum Entropy dan Support Vector Machine,” IJCCS (Indonesian J. Comput. Cybern. Syst., vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 91–100, Jan. 2014.
[5] M. Lailiyah, “Sentiment Analysis Menggunakan Rule Based Method Pada Data Pengaduan Publik Berbasis Lexical Resources,” Aug. 2017.
[6] I. M. D. Ardiada, M. Sudarma, and D. Giriantari, “Text Mining pada Sosial Media untuk Mendeteksi Emosi Pengguna Menggunakan Metode Support Vector Machine dan K-Nearest Neighbour,” Maj. Ilm. Teknol. Elektro, vol. 18, no. 1, p. 55, May 2019.
[7] P. S. M. Suryani, L. Linawati, and K. O. Saputra, “Penggunaan Metode Naïve Bayes Classifier pada Analisis Sentimen Facebook Berbahasa Indonesia,” Maj. Ilm. Teknol. Elektro, vol. 18, no. 1, p. 145, May 2019.
[8] M. R. Huq, A. Ali, and A. Rahman, “Sentiment Analysis on Twitter Data using KNN and SVM,” IJACSA) Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl., vol. 8, no. 6, pp. 19–25, 2017.
[9] H. Peng et al., “Tensor Fusion Network for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis,” IJCCS (Indonesian J. Comput. Cybern. Syst., vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 147–156, 2017.
[10] N. L. Ratniasih, M. Sudarma, and N. Gunantara, “Penerapan Text Mining Dalam Spam Filtering Untuk Aplikasi Chat,” Maj. Ilm. Teknol. Elektro, vol. 16, no. 3, p. 13, Dec. 2017.
[11] N. G. Yudiarta, M. Sudarma, and W. G. Ariastina, “Penerapan Metode Clustering Text Mining Untuk Pengelompokan Berita Pada Unstructured Textual Data,” Maj. Ilm. Teknol. Elektro, vol. 17, no. 3, p. 339, Dec. 2018.
[12] A. A. Magriyanti, “Analisis Pengembangan Algoritma Porter Stemming Dalam Bahasa Indonesia,” Attrib. 4.0 Int., 2018.
[13] I. M. A. Agastya, “Pengaruh Stemmer Bahasa Indonesia Terhadap Peforma Analisis Sentimen Terjemahan Ulasan Film,” J. Tekno Kompak, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 18–23, Feb. 2018.
[14] C. Lu, D. Wang, X. Liu, and K. Gan, “A mining and visualizing system for large-scale Chinese technical standards,” in Proceedings - IEEE 4th International Conference on Big Data Computing Service and Applications, BigDataService 2018, 2018, pp. 1–8.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License