Disain Turbin Model Nest-Lie Untuk Mikro Hidro
Abstract
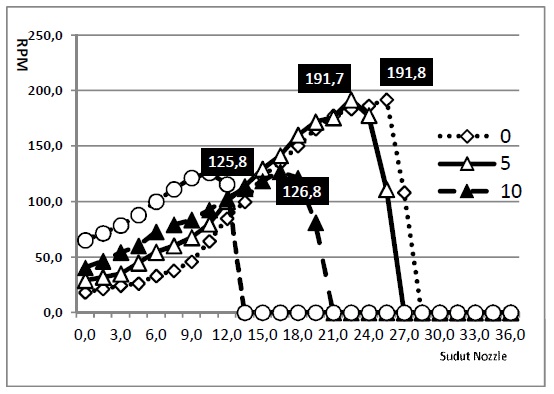
Abstract — Air merupakan salah satu sumber energi yang potesinnya besar dan tersebar di seluruh wilayah Indonesia. Masalah utama dari pembangkit tenaga air adalah debit air yang mengalir tidak kontinyu sepanjang tahun. Karakteristik lokasi masing-masing penempatan mikro hidro adalah unik. Sebuah mikro hidro yang ditempatkan pada lokasi tertentu diperlukan turbin yang sesuai dengan karakteristik lokasi yang ada. Dalam penelitian ini dirancang turbin untuk mendapatkan turbin model Nest-Lie jenis baru yang mengakomodir semua parameter lokasi yang ada. Metode yang dilakukan adalah (1). Memanfaatkan data lokasi untuk isiaiasi desain awal, (2). menemukan model matematis turbin, (3). membuat prototipe model untuk diuji di laboratorium, (4). Membuat model turbin yang sebenarnya untuk ujicoba lapangan. Hasil yang didapat dari penelitian ini adalah RPM pada roda turbin Nest-Lie menghasilkan perbedaan yang sangat signifikan, dengan tekanan pada 28 Psi yang terbaca pada menghasilkan RPM berkisar antara 157,2 -231,1 dimana sudut posisi untuk 0o. 5o, 10o, 15o. RPM tertinggi untuk sudut posisi 0o dan dengan pada sudut nozzle 22,5o. dan Sudut nozzle yang menghasilkan RPM tertinggi adalah pada sudut 22,5-25,5 dengan sudut posisi 0o-5o. Tekanan yang dihasilkan pada saluran nozzle bukan merupakan penjumlahan dari tekanan masing-masing, hanya terjadi peningkatan sebesar 27%. Dan RPM mengalami peningkatan sebesar 20%.
Kata Kunci— Mikro hidro, Turbin, Cross flow, Nest-lie
Downloads
References
[2] K. Smail and B. Andrew, “Best Practices for Sustainable Development of Micro hydro Power in Development Countries,” The Department for International Development, UK and The World Bank, UK, Final Report, Mar. 2000.
[3] A. Prayitno, A. Awaluddin, and A. Anhar, “Renewable energy mapping at Riau Province: Promoting Energy Diversification for sustainable development (a case study),” presented at the 2010 Proceedings of the International Conference on Energy and Sustainable Development: Issues and Strategies (ESD), 2010, pp. 1 –4.
[4] G. P. Harrison and H. W. Whittington, “Investment in renewable energy: accounting for climate change,” in 2002 IEEE Power Engineering Society Summer Meeting, 2002, vol. 1, pp. 140 –144 vol.1.
[5] I. Ushiyama, “Renewable energy strategy in Japan,” Renew. Energy, vol. 16, no. 1–4, pp. 1174–1179, Jan. 1999.
[6] Z. Naibo, S. Shingyi, and H. Zhengli, “Small-scale hydropower in China,” Biomass, vol. 20, no. 1–2, pp. 77–102, 1989.
[7] S. P. Adhau, “A comparative study of micro hydro power schemes promoting self sustained rural areas,” in International Conference on Sustainable Power Generation and Supply, 2009. SUPERGEN ’09, 2009, pp. 1 –6.
[8] T. H. Ching, T. Ibrahim, F. I. A. Aziz, and N. M. Nor, “Renewable energy from UTP water supply,” in 2011 International Conference on Electrical, Control and Computer Engineering (INECCE), 2011, pp. 142 –147.
[9] M. Pigaht and R. J. van der Plas, “Innovative private micro-hydro power development in Rwanda,” Energy Policy, vol. 37, no. 11, pp. 4753–4760, Nov. 2009.
[10] O. Paish, “Small hydro power: technology and current status,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 6, no. 6, pp. 537–556, Dec. 2002.
[11] M. Djiteng, Pembangkitan Energi Listrik. Jakarta: Erlangga, 2005.
[12] L. Jasa, A. Priyadi, and M. H. Purnomo, “Designing angle bowl of turbine for Micro-hydro at tropical area,” in 2012 International Conference on Condition Monitoring and Diagnosis (CMD), Sept., pp. 882–885.
[13] L. Jasa, P. Ardana, and I. N. Setiawan, “Usaha Mengatasi Krisis Energi Dengan Memanfaatkan Aliran Pangkung Sebagai Sumber Pembangkit Listrik Alternatif Bagi Masyarakat Dusun Gambuk –Pupuan-Tabanan,” in Proceding Seminar Nasional Teknologi Industri XV, ITS, Surabaya, 2011, pp. B0377–B0384.
[14] U. Navon, I. Zur, and D. Weiner, “Simulation model for optimising energy allocation to hydro-electric and thermal plants in a mixed thermal/hydro-electric power system,” Gener. Transm. Distrib. Iee Proc. C, vol. 135, no. 3, pp. 182 –188, May 1988.
[15] S. Soares and C. T. Salmazo, “Minimum loss predispatch model for hydroelectric power systems,” Ieee Trans. Power Syst., vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 1220 –1228, Aug. 1997.
[16] M. Mohibullah, A. M. Radzi, and M. I. A. Hakim, “Basic design aspects of micro hydro power plant and its potential development in Malaysia,” in Power and Energy Conference, 2004. PECon 2004. Proceedings. National, 2004, pp. 220 – 223.
[17] R. E. Doan and K. Natarajan, “Modeling and control design for governing hydroelectric turbines with leaky Wicket gates,” Ieee Trans. Energy Convers., vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 449 – 455, Jun. 2004.
[18] E. De Jaeger, N. Janssens, B. Malfliet, and F. Van De Meulebroeke, “Hydro turbine model for system dynamic studies,” Ieee Trans. Power Syst., vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 1709 –1715, Nov. 1994.
[19] T. Sakurai, H. Funato, and S. Ogasawara, “Fundamental characteristics of test facility for micro hydroelectric power generation system,” presented at the International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, 2009. ICEMS 2009, 2009, pp. 1 –6.
[20] I. F. G. Garcia, S. R. Lozano, and O. P. H. De La O, “Development of a Real Time Simulator to Test Load and Speed Control Systems of Hydroelectric Power Plants,” in International Conference on Electrical, Communications, and Computers, 2009. CONIELECOMP 2009, 2009, pp. 250 –255.
[21] A. Wijesinghe and L. L. Lai, “Small hydro power plant analysis and development,” in 2011 4th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT), 2011, pp. 25 –30–.
[22] L. M. O. de Mesquita, J. dos Santos Menas, E. L. van Emmenk, and M. Aredes, “Maximum power point tracking applied on small hydroelectric power plants,” in 2011 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), 2011, pp. 1 –6.
[23] L. Jasa, Ika Putri, A. Priyadi, and M. H. Purnomo, “Design optimization of micro hydro turbine using artificial particle swarm optimization and artificial neural network,” Kursor, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 135–144, oktober 2014.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License