Sistem Inspeksi Visual Penempatan Label Produk Lip Cream Line Menggunakan Metode Deep Learning
Abstract
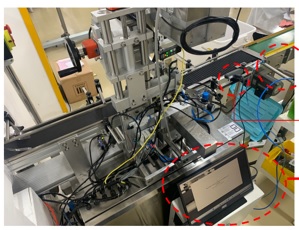
SBL (Single Bottom Labeller) machine which was still not precise for placing the bottom label batches of lip cream products. Postal operators must then check one by one to ensure product quality control so that there are bottlenecks. Therefore, this research uses the YOLOv5 deep learning method to solve this problem. The YOLOv5 algorithm uses the idea of regression, making it easier to learn generalizations, target characteristics and solve speed problems. The YOLO algorithm uses a one-stage neural network to complete the localization and classification of detected objects in real time. The core idea of YOLO is to take the entire image as network input and directly return the bounding box position and bounding box class in the output. In YOLO, each bounding box is predicted by the features of the entire image, and each bounding box contains the five predictions and a confidence, which is relative to the grid cell in the middle of the bounding box. The results of research using the YOLOv5 method can classify into three classification categories of bottom label placement, namely accept, reject and no label. In addition to classifying, this study will also send triggers to the controller if the bottom label is said to be rejected and no label to do product sorting to assist QC operators in sorting lip cream production defects.
Downloads
References
[2] E. R. Setyaningsih and M. S. Edy, “YOLOv4 dan Mask R-CNN Untuk Deteksi Kerusakan Pada Karung Komoditi,” Teknika, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 45–52, Mar. 2022, doi: 10.34148/teknika.v11i1.419.
[3] Q. Aini, N. Lutfiani, H. Kusumah, and M. S. Zahran, “Deteksi dan Pengenalan Objek Dengan Model Machine Learning: Model Yolo,” CESS J. Comput. Eng. Syst. Sci., vol. 6, no. 2, p. 192, Jul. 2021, doi: 10.24114/cess.v6i2.25840.
[4] D. R. Wilson and T. R. Martinez, “The need for small learning rates on large problems,” in IJCNN’01. International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Proceedings (Cat. No. 01CH37222), vol. 1. IEEE, 2001, pp. 115–119.
[5] P. M. Radiuk, “Impact of training set batch size on the performance of convolutional neural networks for diverse datasets,” 2017.
[6] Baudet, N., Maire, J.C., and Pillet, M., 2012. The Visual Inspection of Product Surface. Food Quality and Preference.
[7] Ramos, M., Valdes, A., and Garrigos, M.A., 2016. Packaging for Drinks. Reference Modul in Food Science: Analytical Chemistry, Nutrition & Food Science. University of Alicante, Spain.
[8] Wang, J., Fu, P., and Gao, RX., 2019. Machine Vision Intelligence for Product Defect Inspection Based on Deep Learning and Hough Transform, Journal of Manufacturing System, 51: 52-60.
[9] Liang, Q., Zhu, W., Sun, W., Yu, Z., Wang, Y., and Zhang, D., 2019. In Line Inspection Solution for Codes on Complex Background for The Plastic Container Industry, Journal of Measurement, 148, 106965.
[10] Perez, H., Joseph, H., Tah, M. and Mosavi, A., 2019. Deep Learning for Detecting Building Defects Using Convolutional Neural Network, MDPI Journal.
[11] Panella, F., Boehm, J., Loo, Y., Kaushik, A., and Gonzales, D., 2018. Deep Learning and Image Processing for Automated Crack Detection and Defect Measurement in Underground Structures, Journal of Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Volume: XLII-2.
[12] Costa, A.Z., Hugo, E.H.F., and Fracarolli, J.A., 2020. Computer Vision Based Detection of External Defects on Tomatoes using Deep Learning, Journal of Biosystem Engineering, 190: 131-144.
[13] Rokhana, R., Priambodo, J., Karlita, T., Sunarya, I.M.G., Yuniarto, E.M., Purnama, I.K.E., dan Purnomo, M.H., 2019. Convolutional Neural Network untuk Pendekteksian Patah Tulang Femur pada Citra Ultrasonik B-Mode, JNTETI, Volume 8, No.1.
[14] LeCun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., and Haffner, P., 1998. Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition, Proceeding of the IEEE, Vol.86, No.11, 2278-2324.
[15] Simonyan, K., and Zisserman, A., 2014. Very Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Large-Scale Image Recognition, ArXiv140091556Cs.
[16] Zhang, X., Zhou, X., Lin., M, and Sun, J., 2018. ShuffleNet: An Extremely Efficient Convolutional Neural Network for Mobile Devices, CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE.
[17] Rezende, E., Ruppert, G., Carvalho, T., Ramos, F., and Geus, P.D., 2017. Malicious Sofware Classification using Transfer Learning of ResNet-50 Deep Neural Network, Conference on Machine Learning & Applications, 16th.
[18] Wang, J., May, Y., Zhang, I., Gao, R.X., and Wu, D., 2018. Deep Learning for Smart Manufacturing: Methods and Applications, Journal of Manufacturing System, 48: 144-16.
[19] Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., Sermanet, P., Reed, S., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Vanhoucke, V., and Rabinovich, A., 2015. Going Deeper with Convolutional, IEEE, 978-1-4673-6964-0/15.
[20] He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., and Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. Conference on Computer Vision add Pattern Recognition, IEEE.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License